24/7 Trading A New Era of Trading on the Horizon
 The concept of round-the-clock trading has gained significant traction, inspired partly by the seamless 24/7 operations of cryptocurrency markets and a notable surge in retail investor activity, catalyzed by the global pandemic. As the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) explores the feasibility of extending trading hours for stocks like Nvidia or Apple into the overnight sessions, the financial landscape stands at the precipice of a transformative shift.
The concept of round-the-clock trading has gained significant traction, inspired partly by the seamless 24/7 operations of cryptocurrency markets and a notable surge in retail investor activity, catalyzed by the global pandemic. As the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) explores the feasibility of extending trading hours for stocks like Nvidia or Apple into the overnight sessions, the financial landscape stands at the precipice of a transformative shift.
The NYSE’s Proactive Approach
Recently, the NYSE, operated by the Intercontinental Exchange, initiated a survey among market participants to gauge the interest in and implications of a 24-hour trading environment. This initiative reflects a proactive approach to understanding the evolving needs of traders and investors, driven by broader trends in global financial markets that already accommodate round-the-clock trading in other sectors such as US Treasuries and major currencies.
The Catalysts Behind Extended Trading Hours
The move towards a 24/7 trading model has been spurred by several factors:
- Cryptocurrency Influence: The ability to trade digital assets at any hour has set a precedent that is increasingly appealing to stock traders, especially among the tech-savvy and younger demographics.
- Global Participation: Extended hours would allow investors from different time zones to engage with the market more conveniently, potentially increasing participation from Asian markets during their daytime.
- Retail Trading Surge: Platforms like Robinhood and Interactive Brokers have already tapped into this demand by offering extended trading hours, using mechanisms like matching trades with internal holdings or through alternative trading systems such as dark pools.
Implications for Brokers and Trading Platforms
For firms like Loffa, the potential shift to a 24/7 trading model presents both opportunities and challenges:
- Technology and Infrastructure: Brokerages will need to enhance their technological infrastructure to support continuous trading, ensuring robust, secure, and efficient systems are in place.
- Customer Support and Services: Extending trading hours means round-the-clock support for traders, requiring expanded customer service capabilities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Continuous trading could complicate compliance with trading regulations and monitoring, necessitating advanced solutions that can handle the increased complexity.
Market Volatility and Liquidity Risk
 Transitioning to a 24/7 trading environment introduces a unique set of challenges and risks that differ significantly from those in a traditional market that closes nightly. Here are key risk factors and how they could change in a non-stop trading landscape:
Transitioning to a 24/7 trading environment introduces a unique set of challenges and risks that differ significantly from those in a traditional market that closes nightly. Here are key risk factors and how they could change in a non-stop trading landscape:
In a 24/7 environment, market volatility could increase due to extended trading hours. Price fluctuations might become more frequent and unpredictable as global news and events can impact markets instantaneously and at any time. This continuous exposure means that:
- Liquidity management becomes crucial: Brokers must ensure they can manage liquidity effectively at all times to handle sudden market moves without substantial impacts.
- Global market interactions intensify: As different time zones overlap, the reaction to international market events could cause more pronounced volatility, demanding more dynamic and responsive risk management strategies.
Operational Risk
The demand for constant operational readiness elevates the importance of robust infrastructure:
- System uptime and reliability are critical: With markets never closing, the need for systems to operate continuously without failure increases. This includes trading platforms, risk management systems, and client support services.
- Cybersecurity risks escalate: Continuous operation increases exposure to cybersecurity threats. The risk of cyber-attacks might increase, necessitating more stringent and always-on security protocols and real-time threat detection systems.
Counterparty Risk
In a 24/7 trading environment, the assessment of counterparty risk must be continuous:
- Constant evaluation: The ability to assess the creditworthiness and operational stability of trading partners round-the-clock becomes necessary.
- Global exposure: Interacting with more global counterparts can introduce varying levels of risk, including those associated with regulatory compliance and financial stability in different jurisdictions.
Regulatory and Compliance Risk
Regulatory oversight would need to adapt to a non-stop market, potentially leading to new compliance requirements:
- Continuous compliance monitoring: Compliance frameworks would need to be active at all times, aligning with the constant flow of trade data and the need for real-time reporting and monitoring.
- Global compliance challenges: Navigating the compliance requirements of multiple global jurisdictions simultaneously becomes more complex, requiring sophisticated compliance strategies that can adapt to diverse regulatory landscapes.
Human Resource Risk
 Maintaining a workforce capable of supporting a 24/7 operation presents its own challenges:
Maintaining a workforce capable of supporting a 24/7 operation presents its own challenges:
- Shift work and staffing: Ensuring that qualified staff are available at all hours, which could lead to increased costs and the need for shift-based work schedules, impacting employee health and work-life balance.
- Decision fatigue and errors: Prolonged hours could increase the likelihood of human error, requiring enhanced training and possibly greater reliance on automated systems to reduce risk.
Technology and Infrastructure Risk
The need for advanced technological infrastructure becomes more pronounced:
- Dependence on technology: A higher reliance on automated systems and AI to manage operations may lead to vulnerabilities if these systems fail or experience anomalies.
- Technology obsolescence: Rapid technological advances could require frequent updates to systems and software, increasing the costs and operational challenges associated with staying current.
Adopting a 24/7 trading environment significantly alters the risk landscape for financial institutions. The extension of trading hours necessitates robust, flexible systems capable of adapting to the continuous market flux, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and stringent regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions. Brokers and other financial entities must strategically address these risks by investing in technology and infrastructure, developing comprehensive risk management frameworks, and ensuring they have the skilled personnel necessary to operate effectively around the clock. This shift, while challenging, also offers substantial opportunities for those prepared to innovate and adapt in the evolving financial marketplace.
Shifting to a 24/7 trading environment elevates various risks primarily due to the non-stop nature of operations, which can exacerbate vulnerabilities in market operations, compliance, and security. Here’s a summarized explanation of why risks are higher, accompanied by a hypothetical example of how these risks might be exploited:
Increased Risks in a 24/7 Trading Environment

- Extended Market Hours:
- Continual volatility: Extended hours mean more time for global events to impact markets, potentially leading to heightened and less predictable volatility.
- Liquidity variations: Liquidity may vary significantly outside traditional trading hours, leading to increased price slippage and wider spreads.
- Operational Demand:
- Constant system and staff readiness: The need for systems and support staff to operate flawlessly around the clock increases the strain on resources and infrastructure.
- Heightened cybersecurity threats: More operating hours mean more opportunities for cyberattacks, with systems needing continuous protection.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Round-the-clock compliance monitoring: Ensuring compliance with trading rules at all times requires more robust and sophisticated monitoring systems.
- Global regulation complexities: Managing compliance with varying international regulations becomes more challenging as trades can occur at any time, potentially overlapping with different regulatory regimes.
Hypothetical Example of Exploiting 24/7 Trading:
Imagine a scenario involving arbitrage manipulation during off-peak hours when liquidity is lower. An unscrupulous trader could exploit the reduced liquidity to manipulate prices of a particular stock or asset class:
- Setting the scene: The trader observes that liquidity for a specific stock drastically drops after traditional market hours, with fewer participants and reduced transaction volumes.
- Manipulation tactic: Utilizing high-frequency trading algorithms, the trader places large buy orders for the stock during these off-peak hours, artificially driving up its price due to the low liquidity.
- Exploiting the spike: Once the price is sufficiently inflated, the trader quickly sells off at the higher price to maximize profits before other market participants react.
- Consequence: This manipulation distorts the market price temporarily but significantly, leading to false market signals and potentially triggering a cascade of automated trades based on the manipulated price.
- Regulatory gap: If regulatory monitoring systems are less effective or slower outside traditional hours, the trader might evade immediate detection, exploiting gaps in surveillance.
This example illustrates how extended trading hours can create opportunities for market manipulation, particularly when traditional safeguards are less effective or when the market’s defensive mechanisms are not fully operational around the clock. Such scenarios underscore the need for brokers and regulatory bodies to enhance their technological and procedural defenses to address the increased risks associated with a 24/7 trading environment.
Loffa’s Strategic Positioning
 At Loffa, we are uniquely positioned to help our clients navigate this potential new landscape. Our cutting-edge SaaS solutions are designed for agility and scalability, allowing rapid adaptation to changes such as those proposed by the NYSE:
At Loffa, we are uniquely positioned to help our clients navigate this potential new landscape. Our cutting-edge SaaS solutions are designed for agility and scalability, allowing rapid adaptation to changes such as those proposed by the NYSE:
- Innovative Software Solutions: We offer platforms that can quickly adjust to extended trading hours, supporting seamless transactions and continuous compliance monitoring.
- Expertise and Support: Our team is prepared to extend our support hours, ensuring that our clients have access to expert assistance whenever the markets are open.
- Proactive Compliance Tools: We provide tools that help our clients stay ahead of regulatory requirements, no matter how the trading schedule shifts.
Impact on Settlement Cycles
Currently, the standard settlement cycle for most securities transactions in the U.S. is T+2, meaning transactions are settled two business days after the trade is executed. With the introduction of 24/7 trading, the concept of “business days” becomes less relevant, potentially leading to the need for daily, if not real-time, settlement processes.
Challenges to Overcome:
- Extended Operation Hours:
- Human Resources: Brokerages would need to staff operational and support functions around the clock, ensuring that all aspects of trade processing, from execution to settlement, are covered continuously.
- System Resilience: IT systems would need to be robust enough to handle a constant flow of trades without downtime for maintenance or batch processing, which traditionally occurs during off-hours.
- Real-Time Risk Management:
- The ability to monitor and manage risk in real-time becomes crucial as the window to address discrepancies or errors shrinks. Systems powered by advanced algorithms and perhaps even AI could provide ongoing risk assessments and fraud detection.
- Compliance and Reporting:
- Regulatory frameworks would need to evolve to address the realities of a non-stop market. Compliance systems must be capable of continuous monitoring and reporting, with AI and automation playing key roles in ensuring brokers remain compliant with all applicable laws and regulations.
Workflow Adjustments for 24/7 Trading
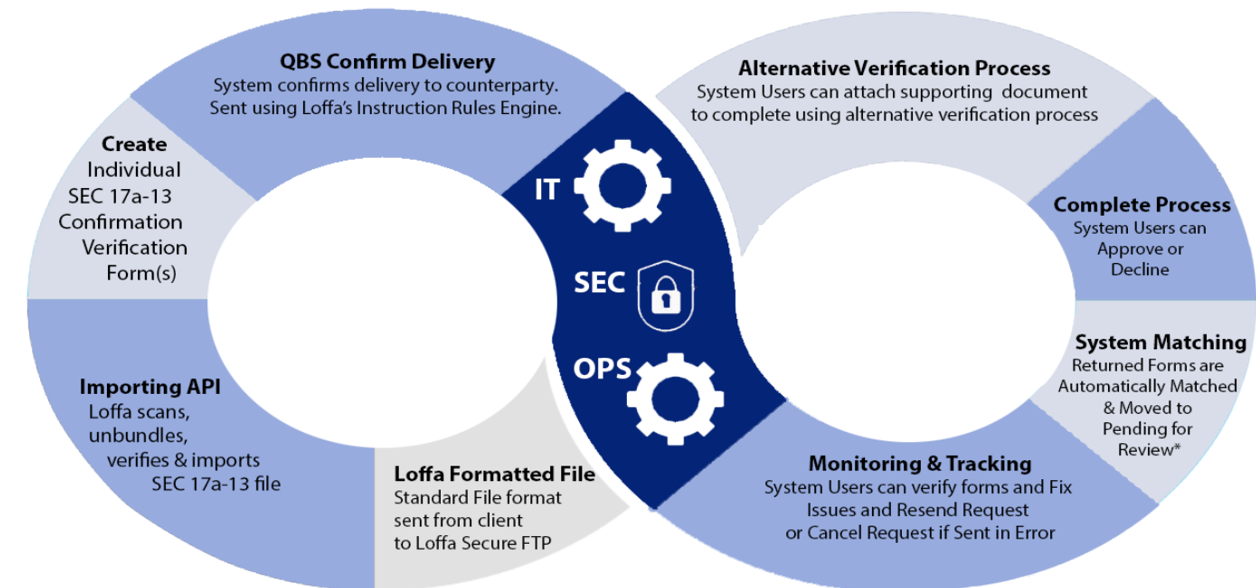 To accommodate a 24/7 trading schedule, brokers would need to implement several strategic workflow adjustments:
To accommodate a 24/7 trading schedule, brokers would need to implement several strategic workflow adjustments:
- Automation of Settlement Processes:
- Emphasizing the automation of settlement and clearing processes to reduce the dependency on manual intervention and to increase efficiency and error handling.
- Implementation of technologies such as distributed ledger technology (DLT) could streamline settlements by reducing the need for reconciliation and expediting the verification processes.
- Enhanced Liquidity Management:
- Brokers would need to ensure that liquidity is managed dynamically to cope with the potential for increased volatility and trading volume, necessitating sophisticated liquidity forecasting tools.
- Continuous Customer Service:
- Providing round-the-clock customer support to address client inquiries and issues instantly, which would be crucial for maintaining client trust and satisfaction in a 24/7 market.
- Adapting to Global Market Participation:
- As trading hours extend, the interaction with global markets will increase. Brokers must be prepared to handle transactions across different time zones and regulatory environments seamlessly.
Technological Upgrades and Integration
The transition to continuous trading would require brokers to invest heavily in technology:
- Scalable Infrastructure: Enhancing data storage and processing capabilities to handle an increased volume of transactions without lag or disruption.
- Advanced Analytics and Reporting Tools: Utilizing sophisticated analytics to generate real-time insights into market trends, trader behavior, and potential compliance issues.
Conclusion: Preparing for the Future
As the dialogue around a 24/7 stock exchange continues to evolve, Loffa remains committed to providing the solutions and support that brokers need to succeed in an ever-changing financial environment. Whether or not the NYSE moves forward with round-the-clock trading, our focus is on enabling our clients to leverage new opportunities, maintain compliance, and offer superior service to their traders and investors.
The potential for a 24-hour trading window represents a significant evolution in stock market operations, echoing the dynamic nature of today’s financial ecosystems. At Loffa, we are excited about the possibilities this presents and are dedicated to helping our clients thrive in this new era of trading.
 In the dynamic world of financial services, brokerages continually search for ways to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. Leveraging innovative technologies plays a pivotal role in this quest, driving significant transformations across brokerage operations.
In the dynamic world of financial services, brokerages continually search for ways to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. Leveraging innovative technologies plays a pivotal role in this quest, driving significant transformations across brokerage operations. Automated risk assessment tools embedded within workflows can instantly analyze the potential impact of trades across various scenarios, providing brokers with immediate feedback on risk exposure. This rapid assessment is essential for making prudent decisions in a market where reaction times are significantly shortened.
Automated risk assessment tools embedded within workflows can instantly analyze the potential impact of trades across various scenarios, providing brokers with immediate feedback on risk exposure. This rapid assessment is essential for making prudent decisions in a market where reaction times are significantly shortened.

 The move from T+2 to T+1 settlement cycles represents a pivotal shift in the financial sector. Aimed at increasing transaction efficiency and reducing exposure to risk, this change is set against a backdrop of global market evolution and technological progress.
The move from T+2 to T+1 settlement cycles represents a pivotal shift in the financial sector. Aimed at increasing transaction efficiency and reducing exposure to risk, this change is set against a backdrop of global market evolution and technological progress. The compliance timeline tightens under T+1. Regulators, both domestic and international, will need to adapt their frameworks to support faster settlements. This scenario requires firms to enhance their compliance systems to meet new operational demands within stringent time constraints.
The compliance timeline tightens under T+1. Regulators, both domestic and international, will need to adapt their frameworks to support faster settlements. This scenario requires firms to enhance their compliance systems to meet new operational demands within stringent time constraints. dvanced technologies like AI and blockchain are set to play a crucial role in facilitating T+1 settlements. Blockchain technology, with its capability for real-time ledger updates, offers a transparent and efficient method for recording transactions, which is ideal for the quick turnaround required in T+1. Similarly, AI can automate and optimize the decision-making processes involved in the settlement, such as identifying potential errors or mismatches in trade data almost instantaneously.
dvanced technologies like AI and blockchain are set to play a crucial role in facilitating T+1 settlements. Blockchain technology, with its capability for real-time ledger updates, offers a transparent and efficient method for recording transactions, which is ideal for the quick turnaround required in T+1. Similarly, AI can automate and optimize the decision-making processes involved in the settlement, such as identifying potential errors or mismatches in trade data almost instantaneously.
 The concept of round-the-clock trading has gained significant traction, inspired partly by the seamless 24/7 operations of cryptocurrency markets and a notable surge in retail investor activity, catalyzed by the global pandemic. As the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) explores the feasibility of extending trading hours for stocks like Nvidia or Apple into the overnight sessions, the financial landscape stands at the precipice of a transformative shift.
The concept of round-the-clock trading has gained significant traction, inspired partly by the seamless 24/7 operations of cryptocurrency markets and a notable surge in retail investor activity, catalyzed by the global pandemic. As the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) explores the feasibility of extending trading hours for stocks like Nvidia or Apple into the overnight sessions, the financial landscape stands at the precipice of a transformative shift. Transitioning to a 24/7 trading environment introduces a unique set of challenges and risks that differ significantly from those in a traditional market that closes nightly. Here are key risk factors and how they could change in a non-stop trading landscape:
Transitioning to a 24/7 trading environment introduces a unique set of challenges and risks that differ significantly from those in a traditional market that closes nightly. Here are key risk factors and how they could change in a non-stop trading landscape: Maintaining a workforce capable of supporting a 24/7 operation presents its own challenges:
Maintaining a workforce capable of supporting a 24/7 operation presents its own challenges:
 At Loffa, we are uniquely positioned to help our clients navigate this potential new landscape. Our cutting-edge SaaS solutions are designed for agility and scalability, allowing rapid adaptation to changes such as those proposed by the NYSE:
At Loffa, we are uniquely positioned to help our clients navigate this potential new landscape. Our cutting-edge SaaS solutions are designed for agility and scalability, allowing rapid adaptation to changes such as those proposed by the NYSE: To accommodate a 24/7 trading schedule, brokers would need to implement several strategic workflow adjustments:
To accommodate a 24/7 trading schedule, brokers would need to implement several strategic workflow adjustments: