The Price of Integrity: Unpacking the Total Cost of Compliance in Finance
7 min read
Understanding the Total Cost of Compliance in Financial Services
In today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, regulatory compliance represents a significant and complex challenge for firms across the spectrum. The Total Cost of Compliance (TCC) has become a critical metric for financial institutions striving to navigate the intricate web of global regulations while ensuring operational efficiency and maintaining competitiveness. This blog post delves into the components of TCC, explores the impact of technological advancements, and highlights strategic considerations for managing these costs effectively.
The Components of Total Cost of Compliance
TCC encompasses direct and indirect costs associated with adhering to regulatory requirements. These include:
- Regulatory Fees and Penalties: Direct costs to regulatory bodies and potential fines for non-compliance.
- Technology Investments: Costs related to purchasing, implementing, and maintaining compliance software and infrastructure.
- Personnel Expenses: Salaries and training costs for compliance staff.
- Consulting and Legal Fees: Expenses for external experts who provide regulatory guidance and support.
- Operational Disruptions: Indirect costs from changes to business processes or strategies to meet compliance standards.
Calculating the costs:
Calculating the Total Cost of Compliance (TCC) in financial services involves a comprehensive analysis of direct and indirect costs associated with adhering to regulatory standards. Here’s a breakdown of various components to consider:
- Compliance Technology and Infrastructure: Investments in software and hardware to facilitate compliance processes, such as transaction monitoring systems, compliance management platforms, encryption technologies, and secure data storage solutions. This also includes the depreciation of these assets over time and the costs of updates or replacements to keep up with evolving regulatory requirements.
- External Consultants and Legal Fees: Costs associated with hiring external experts, such as legal advisors, auditors, and consultants, to ensure compliance practices are up to date and to handle specific regulatory challenges or audits.
- Implementation of Regulatory Changes: The cost of adapting operations to comply with new or amended regulations. This includes project management costs, systems upgrades, process redesign, and the operational impact of adjusting business practices.
- Compliance-Related Communications: Costs associated with creating, distributing, and maintaining required disclosures, privacy notices, and other compliance-related communications to clients.
- Risk Assessments and Audits: The expense of conducting regular internal and external audits and risk assessments to ensure compliance and identify areas of potential risk.
- Penalties and Remediation: Although not a proactive cost, penalties for non-compliance and the cost of remediation efforts post-violation can significantly impact the TCC. Planning for contingencies and setting aside reserves for potential fines is a prudent strategy.
- Opportunity Costs: The indirect costs related to compliance, such as potential business opportunities forgone due to regulatory restrictions or the time management spends on compliance issues instead of core business activities.
- Reputation and Customer Trust: While difficult to quantify, the impact of compliance (or non-compliance) on a firm’s reputation and the trust of its customers can have significant long-term financial implications.
- Data Protection and Privacy Compliance: Costs associated with adhering to data protection regulations such as GDPR or CCPA, including data processing audits, privacy impact assessments, and any necessary changes to data handling processes.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Investments in cybersecurity defenses to comply with regulatory standards on data security, including regular security assessments, penetration testing, and incident response planning.
- Record-Keeping and Reporting Requirements: The operational and technology costs associated with maintaining records in compliance with legal and regulatory mandates, including the storage, retrieval, and submission of reports to regulatory bodies.
- Compliance Training Development: Designing and updating training programs for employees on compliance matters, anti-money laundering (AML) practices, and ethical conduct to ensure understanding and adherence to regulatory expectations.
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Processes: The operational costs related to conducting CDD and KYC checks, including the verification of customer identities and the ongoing monitoring of transactions for suspicious activities.
- Regulatory Change Management: The cost of staying informed about regulatory changes, analyzing their impact on operations, and implementing necessary adjustments in policies, procedures, and systems.
- Whistleblower Programs: Establishing and maintaining systems for internal reporting of potential regulatory violations or unethical conduct, including protections for whistleblowers.
- Insurance: Premiums for insurance policies that cover compliance-related risks, such as professional liability insurance, which may be required or prudent given the regulatory environment.
- Technology Upgrades for Compliance Agility: Investments in technology that enhance the firm’s ability to quickly adapt to regulatory changes, such as flexible compliance management systems or AI-driven analytics for detecting non-compliant activities.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Compliance: Costs related to developing, implementing, and reporting on ESG policies and practices, as regulatory focus on sustainable finance and responsible investing grows.
- Consultancy Fees: Fees paid to external consultants for advice on compliance matters, interpretation of regulatory requirements, and assistance during regulatory examinations or investigations.
- Environmental Compliance Costs: Expenses related to complying with environmental regulations, including waste management, emissions controls, and reporting on environmental impact.
- Operational Resilience Planning: Investments in building systems and processes to ensure operational continuity in the face of disruptions, in compliance with emerging regulations focused on operational resilience.
- Cross-border Compliance: Costs associated with understanding and adhering to regulations in every jurisdiction the firm operates in, including international data transfer rules and foreign investment regulations.
- Third-party Vendor Management: Expenses related to the due diligence, monitoring, and management of third-party vendors to ensure they comply with relevant regulations and do not expose the firm to compliance risks.
- Business Continuity Planning: Costs associated with developing, testing, and maintaining business continuity plans to ensure the firm can continue critical operations during and after a disruption, in compliance with regulatory requirements for operational resilience and disaster recovery planning.
- Regulatory Fees and Licenses: Direct costs to obtain necessary licenses and fees paid to regulatory bodies. This includes initial licensing fees, annual renewals, and any costs associated with maintaining special registrations.
- Compliance Personnel: Salaries, benefits, and training costs for compliance staff. Consider the number of personnel required based on the firm’s size, complexity, and the regulatory landscape it operates within. Training costs should also factor in ongoing education to stay abreast of regulatory changes.
Estimated costs:
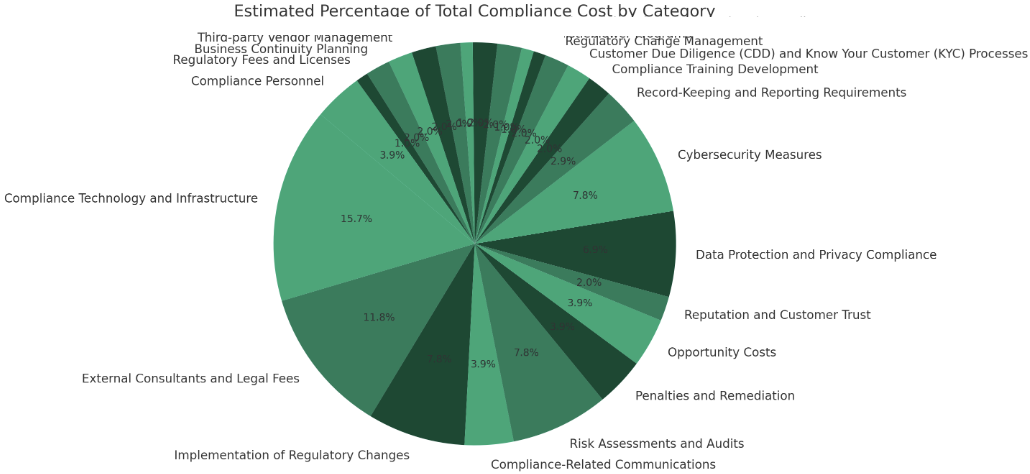
- Compliance-Related Communications: 4%
- Risk Assessments and Audits: 8%
- Compliance Technology and Infrastructure: 16%
- External Consultants and Legal Fees: 12%
- Implementation of Regulatory Changes: 8%
- Penalties and Remediation: 4%
- Opportunity Costs: 4%
- Reputation and Customer Trust: 2%
- Data Protection and Privacy Compliance: 7%
- Cybersecurity Measures: 8%
- Record-Keeping and Reporting Requirements: 3%
- Compliance Training Development: 2%
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Processes: 2%
- Regulatory Change Management: 2%
- Whistleblower Programs: 1%
- Insurance: 1%
- Technology Upgrades for Compliance Agility: 2%
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Compliance: 2%
- Environmental Compliance Costs: 1%
- Operational Resilience Planning: 2%
- Cross-border Compliance: 2%
- Third-party Vendor Management: 2%
- Business Continuity Planning: 2%
- Regulatory Fees and Licenses: 1%
- Compliance Personnel: 4%
The Impact of Technology
 Technological advancements have profoundly transformed the compliance landscape, offering new tools and methodologies to streamline processes and reduce costs. Innovative solutions such as regulatory technology (RegTech) utilize artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics to automate compliance tasks, enhance reporting accuracy, and improve risk management. These technologies can significantly lower the TCC by:
Technological advancements have profoundly transformed the compliance landscape, offering new tools and methodologies to streamline processes and reduce costs. Innovative solutions such as regulatory technology (RegTech) utilize artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics to automate compliance tasks, enhance reporting accuracy, and improve risk management. These technologies can significantly lower the TCC by:
- Automating Routine Tasks: Reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing human error.
- Enhancing Data Management: Improving the accuracy and accessibility of compliance-related data.
- Streamlining Reporting: Automating the generation and submission of regulatory reports.
- Facilitating Real-time Monitoring: Allowing for continuous oversight of compliance status and quicker responses to potential issues.
Strategic Considerations for Managing TCC
- Leverage Technology: Invest in RegTech solutions that align with your firm’s specific compliance needs and operational workflows. Prioritize scalable and integrable technologies that can adapt to regulatory changes.
- Optimize Compliance Processes: Regularly review and streamline compliance procedures to eliminate redundancies and inefficiencies. Embrace a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
- Enhance Training Programs: Invest in comprehensive training for compliance and operational staff to ensure they understand regulatory requirements and the role of technology in compliance processes.
- Collaborate with Regulators: Engage in dialogue with regulatory bodies to gain insights into forthcoming regulations and compliance best practices. Participating in industry forums can also provide valuable knowledge sharing opportunities.
- Monitor Regulatory Developments: Stay informed about changes in the regulatory landscape to anticipate and prepare for compliance challenges. Utilize technology to track and analyze regulatory updates efficiently.
Conclusion
The Total Cost of Compliance is a significant concern for financial services firms, impacting not just financial but also operational and strategic dimensions of business. By understanding the components of TCC and leveraging technological advancements, firms can devise effective strategies to manage these costs, ensuring compliance, operational efficiency, and sustained growth in the complex regulatory environment.